Estimated Reading Time: 5 minutes
In recent years, edge computing and cloud computing have emerged as two crucial concepts in the world of modern technology. As businesses and individuals alike continue to generate more data, understanding the distinctions and advantages of these two computing models is essential. While both offer significant benefits, they serve different purposes and excel in different scenarios. In this article, we’ll explore what edge computing is, how it differs from cloud computing, and why it’s becoming increasingly important for businesses to understand the difference.
Understanding Edge Computing: What It Is and How It Works
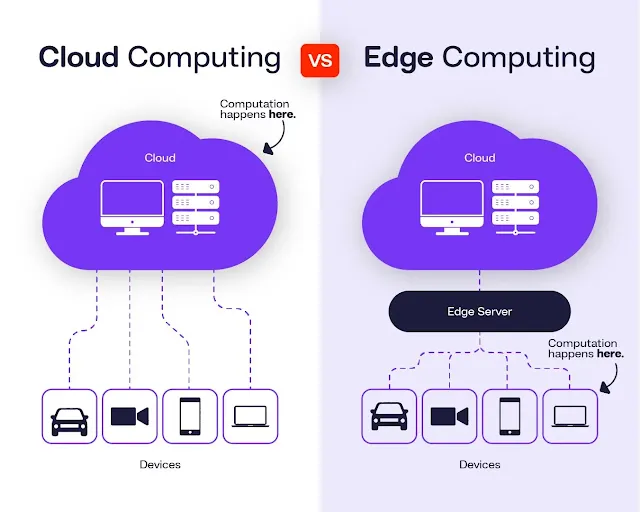
Edge computing refers to the process of bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed—often referred to as the "edge" of the network. Instead of relying on a centralized cloud server located far away, edge computing processes data locally, either on devices or nearby edge servers. This decentralized approach allows for faster processing, reduced latency, and less reliance on a central data center.
Key Features of Edge Computing:
- Low Latency: One of the biggest advantages of edge computing is its ability to reduce latency. By processing data near the source, edge computing minimizes the time it takes to send data to a central server and back.
- Real-Time Processing: Edge computing is ideal for applications that require real-time data processing, such as self-driving cars, remote monitoring systems, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
- Data Sovereignty: Since data can be processed locally, edge computing can offer better control over data privacy and regulatory compliance, particularly in industries that deal with sensitive information.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing, on the other hand, is the practice of storing and processing data on remote servers that can be accessed over the internet. These servers are typically located in centralized data centers and are maintained by cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their IT infrastructure without investing in physical hardware, offering flexibility and ease of access to computing resources.
Key Features of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Cloud computing provides virtually unlimited resources that can be scaled up or down depending on demand. This flexibility makes it ideal for businesses that need to quickly adjust their computing capacity.
- Centralized Storage: With cloud computing, data is stored in centralized data centers, which means businesses don’t have to worry about maintaining physical infrastructure.
- Cost-Efficiency: Since cloud computing uses a pay-as-you-go model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, making it a cost-effective option for many.
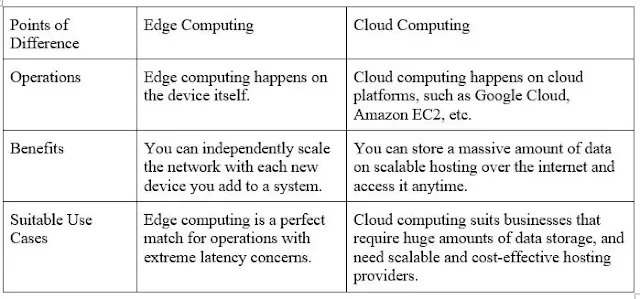
Key Differences Between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
While both edge computing and cloud computing play essential roles in modern IT infrastructure, their differences become clear when you look at their specific purposes and applications.
1. Data Processing Location
- Edge Computing: Data is processed near the source of generation, such as on devices or local edge servers.
- Cloud Computing: Data is processed on centralized servers located in data centers, often far from the user.
2. Latency
- Edge Computing: Offers low latency, as data is processed locally, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time responses.
- Cloud Computing: Typically higher latency, as data has to travel to and from remote servers.
3. Bandwidth Usage
- Edge Computing: Reduces bandwidth consumption since only necessary data is sent to the cloud, while much of the processing happens locally.
- Cloud Computing: Can lead to higher bandwidth usage as large amounts of data must be transferred to and from the cloud.
4. Use Cases
- Edge Computing: Best suited for IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real-time monitoring.
- Cloud Computing: Ideal for web hosting, big data analysis, machine learning, and applications that don’t require real-time data processing.
5. Cost
- Edge Computing: Can be more cost-effective in cases where real-time processing and reduced data transmission are critical. However, it may require investment in edge devices or local servers.
- Cloud Computing: Typically more cost-effective for businesses that need flexible, on-demand computing resources but may incur higher costs due to data transfer.
When to Use Edge Computing and When to Use Cloud Computing?
Both edge computing and cloud computing have their unique advantages, and in many cases, businesses may use them together in a hybrid model to get the best of both worlds. However, the decision of which to use depends on the specific needs of the business or application.
Edge Computing is Ideal for:
- Applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and remote sensors.
- Industries dealing with large amounts of data at the source, like manufacturing and healthcare, where decisions must be made quickly.
- Rural or remote areas with limited internet connectivity, where cloud solutions might be impractical.
Cloud Computing is Ideal for:
- Web-based applications and software as a service (SaaS) solutions, which require scalable infrastructure and access to powerful computing resources.
- Businesses needing to process large datasets that don’t require immediate real-time feedback.
- Companies looking for a cost-effective, centralized system without investing in physical infrastructure.
Combining Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
In today’s interconnected world, many organizations are moving towards a hybrid approach, using both edge and cloud computing in tandem. By combining the local data processing of edge computing with the powerful storage and analytics capabilities of cloud computing, businesses can optimize their operations for both speed and scalability.
Benefits of the Hybrid Approach:
- Enhanced Performance: Edge computing handles real-time processing and reduces latency, while cloud computing provides deep analytics and storage.
- Increased Flexibility: Businesses can choose where to process data depending on the requirements of the application.
- Better Cost Efficiency: Edge computing can reduce the load on cloud servers, lowering costs associated with data transmission and cloud storage.
Edge computing and cloud computing are both indispensable technologies in today’s digital landscape, and understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions about which solution to implement. While edge computing is best suited for applications that demand real-time data processing with minimal latency, cloud computing excels in providing scalable and centralized solutions for a wide range of business needs. By embracing a hybrid approach, organizations can leverage the strengths of both to create a more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective infrastructure.
As data-driven technologies like IoT, AI, and autonomous systems continue to evolve, the role of edge computing will only grow in importance. It’s clear that both edge and cloud computing will play pivotal roles in shaping the future of technology, and knowing when and how to use them will help businesses stay competitive in a fast-paced, data-driven world.
Reference Source:
https://stlpartners.com/articles/edge-computing/edge-computing-vs-cloud-computing/
https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/difference-between-cloud-and-edge-computing/
https://learning.linkedin.com/resources/learning-tech/edge-vs-cloud-computing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jn9yBBymXbQ&pp=ygUNI2NvbXB1dGVyZWRnZQ%3D%3D

.webp)
.webp)