Estimated Reading Time: 5 minutes
How to Check Your Computer's System Information
Understanding your computer's system information is essential for troubleshooting, upgrading hardware, or simply getting to know your device better. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a professional, or just someone looking to make sure your computer is running smoothly, knowing how to check your system's specifications is crucial. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to check your computer's system information on various platforms, providing detailed instructions for Windows, macOS, and Linux users. We’ll also explore some of the most common system specs you may need to know.
Checking System Information on Windows
Windows provides several ways to view your system information, but the most common methods are through the System Information tool, Task Manager, and Settings.
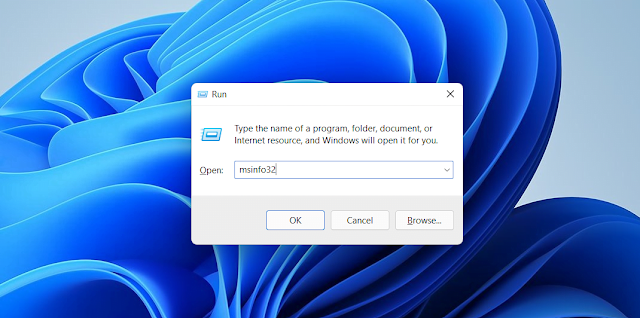
1. Using the System Information Tool
The System Information Tool gives you a comprehensive overview of your system’s details. Here’s how to access it:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type msinfo32 and hit Enter.
- The System Information window will open, displaying details like your operating system version, RAM size, processor type, and more.
Key Information You Can Find Here:
- Operating System: Version, build, and architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Processor: Type, speed, and number of cores.
- Memory: Installed RAM and available memory.
- Graphics: Information about your GPU.
- Storage: Disk size, usage, and partitions.
2. Using Task Manager
For a quick check of your CPU and memory performance:
- Right-click the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Go to the Performance tab to see real-time data on CPU, RAM, disk, and GPU usage.
3. Using Settings
For a basic view of your system:
- Go to Settings > System > About.
- Under the Device specifications section, you can find your processor, RAM, and system type.
How to Check System Information on macOS
macOS provides an easy way to view your system specs through the About This Mac feature. This method is user-friendly and delivers all the essential information in one place.
1. Using “About This Mac”
To view your Mac’s system information:
- Click on the Apple logo in the top-left corner.
- Select About This Mac from the dropdown menu.
- A window will pop up showing details like your macOS version, processor, RAM, and graphics.
Key Details You’ll Find Here:
- macOS Version: The operating system version and build.
- Processor: Model and speed.
- Memory: Total RAM installed and available.
- Storage: Information on your hard drive and its usage.
2. Using System Report for Advanced Details
If you want more detailed hardware information:
- From the About This Mac window, click on System Report.
- This will open a more detailed overview of your hardware, including network information, storage devices, and even peripherals connected to your Mac.
Checking System Information on Linux
Linux users have a variety of ways to check system specs, whether through command-line tools or graphical interfaces.
1. Using the Terminal
For advanced users, the terminal provides quick and detailed information about your system.
Command to Check General System Information:
- Open the Terminal and type:
This will show you your kernel version and system architecture.
To Check CPU Information:
- Type:
This provides detailed info on your CPU, such as cores, model name, and architecture.
To Check Memory Information:
- Type:
This command displays memory usage, both used and free memory.
To Check Disk Space:
- Type:
This will show you disk space usage for all mounted file systems.
2. Using Graphical Tools
For those who prefer a graphical interface, many Linux distributions offer System Monitor tools that display hardware usage and specs in an easy-to-read format. You can search for System Monitor or System Info in your distribution's application menu.
Key System Information You Should Know
When checking your computer's system information, these are the most common and important specs to look out for:
1. Processor (CPU)
Your CPU is the brain of your computer. It handles the majority of computations. Key specs include:
- Model: Intel, AMD, or other brands.
- Cores: Number of cores (e.g., dual-core, quad-core).
- Clock Speed: The processing speed of your CPU, measured in GHz.
2. Memory (RAM)
RAM (Random Access Memory) is used by the computer to store data temporarily. More RAM means better multitasking. Key things to check:
- Total Installed RAM: This shows how much memory your system has for running programs.
- Available RAM: This shows how much is free for new applications.
3. Graphics Card (GPU)
The GPU processes visual data. It's essential for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive tasks. Key specs:
- GPU Model: Whether it’s integrated (like Intel) or dedicated (like NVIDIA or AMD).
- VRAM: Video memory size.
4. Storage
The storage size determines how much data you can keep on your computer. It can be either:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Traditional, slower, and larger capacity.
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Faster, more reliable, but generally with less capacity.
5. Operating System
The OS is the software that enables you to interact with your hardware. Key aspects to check include:
- Version: Which version of Windows, macOS, or Linux is installed?
- System Type: Whether your OS is 32-bit or 64-bit.
Reference Source:
- https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/find-information-about-your-device-a66d52c8-3323-44fd-8f34-a9497bb935e1
- https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/system-configuration-tools-in-windows-f8a49657-b038-43b8-82d3-28bea0c5666b
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/msinfo32
- https://support.apple.com/guide/system-information/system-information-user-guide-syspr35536/mac



